As an American citizen, I refuse to comply and eat bugs as some global entities want. I also foresee mass starvation due to mandates for the radical elimination of common synthetic fertilizers. I propose the use of MLE (Moringa leaf extract) powder, which has the potential to greatly contribute to a reduction in the reliance on synthetic fertilizers in agricultural practices. Here are some ways in which MLE powder can help decrease the use of traditional fertilizers:
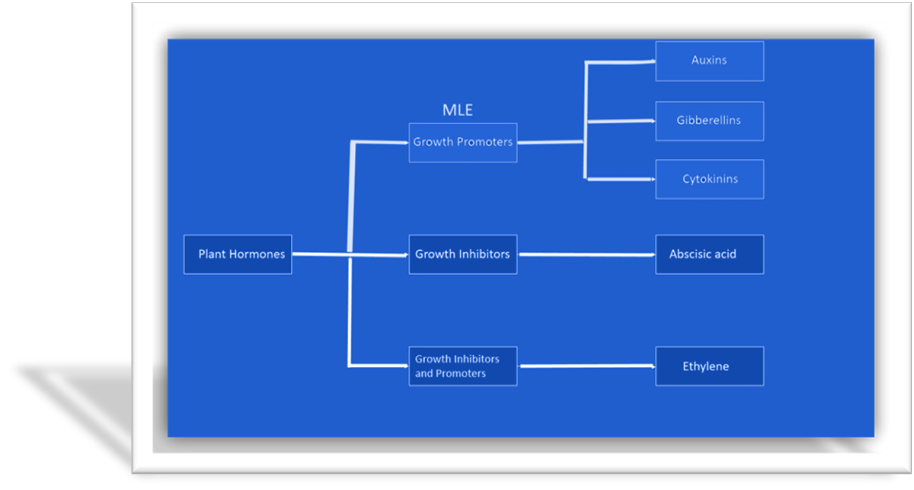
Nutrient Cycling and Soil Microbes: MLE powder promotes nutrient cycling in the soil ecosystem. It stimulates the growth and activity of beneficial soil microorganisms, including nitrogen-fixing bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi. These microorganisms play a crucial role in converting organic matter and atmospheric nitrogen into plant-available forms, reducing the reliance on synthetic nitrogen fertilizers.Slow-Release Nutrients: MLE powder releases nutrients gradually over time, providing a sustained supply of essential elements to plants. This slow-release characteristic helps prevent nutrient leaching and runoff, reducing the potential environmental impact associated with excessive fertilizer use.Enhanced Nutrient Uptake Efficiency: The bioactive compounds present in MLE powder, including cytokinins like zeatin, enhance nutrient uptake efficiency in plants. By stimulating root development and improving nutrient absorption, MLE powder helps plants make better use of available nutrients, minimizing the need for additional fertilizers (Figure 1).
MLE contains many antioxidants and is rich in secondary metabolites and osmoprotectants which help plants survive extreme osmotic stress (Howladar, 2014).
The good manufacturing process of MLE (Moringa leaf extract) powder typically involves several steps. Here is a general outline of the process:

Drying: After washing, the leaves are dried to reduce moisture content. Various drying methods can be employed, including air drying, sun drying, or using low-temperature drying techniques to preserve the nutritional value of the leaves. The drying process may take several hours to several days, depending on the method used.
Extraction: The powdered Moringa leaves are subjected to an extraction process to obtain the bioactive compounds and nutrients. Common extraction methods include solvent extraction, where a suitable solvent (such as water, ethanol, or a mixture of both) is used to dissolve the desired components from the powdered leaves. The extraction may involve heat, agitation, or ultrasonication to enhance the extraction efficiency.Filtration: Once the extraction is complete, the resulting mixture undergoes filtration to remove any solid residues or impurities. Filtration methods such as gravity filtration or filter presses can be used to obtain a clear and refined extract.Concentration: The extracted solution may undergo a concentration step to remove excess solvent and increase the concentration of the bioactive compounds. This can be achieved through methods like evaporation or vacuum drying, where the solvent is evaporated under controlled conditions, leaving behind a concentrated extract.Spray Drying: In some cases, the concentrated Moringa leaf extract is further processed using spray drying. This involves atomizing the concentrated extract into fine droplets, which are then rapidly dried using hot air. The resulting dried particles are collected as a powder. Quality Control and Packaging: The final MLE powder undergoes quality control tests to ensure it meets the desired specifications, such as potency, purity, and microbial safety. Once approved, the powder is packaged in suitable containers to protect it from moisture, light, and air, preserving its quality and shelf life.

